Case Report: Effects of a Vibroacoustic Session on Prefrontal Cortex Activity Using HEG Assessment
Case Submitted by Dr. Francisco Cidral, ND, PhD
Participant Information:Age: 54
Gender: Male
Device Used: BioTekna HEG Performance Device. The BioTekna HEG Performance Device is a non-invasive tool used to assess the activity of the prefrontal cortex. It measures changes in blood flow and oxygenation in the forehead area to evaluate cognitive and emotional function. This helps identify patterns related to stress, attention, and mental performance, making it useful in wellness assessments, clinical evaluations, and research.
Intervention:
- Device: inHarmony Sound Lounge 2 (Vibroacoustic Bed)
- Session: Solfeggio 528 (11 minutes) via inHarmony App
Study Timeline:
- Baseline: Prior to the vibroacoustic session
- Immediate Post-Intervention: After the 11-minute session
- 1 Hour Post-Intervention
- 2 Hours Post-Intervention
Measurements:
|
Parameter |
Baseline |
Post-Session |
1 Hour |
2 Hours |
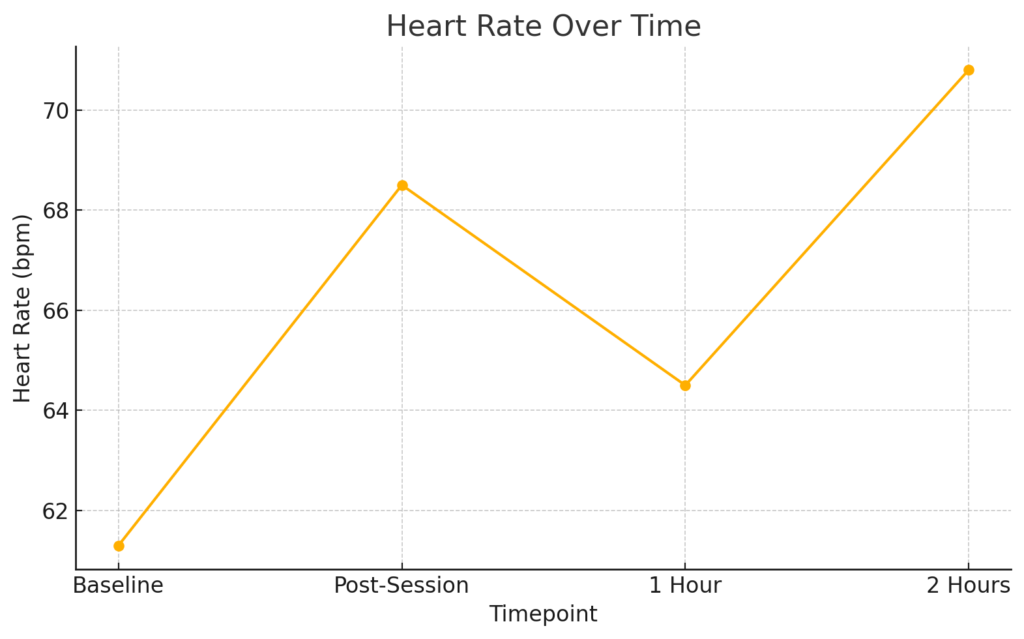
| Heart Rate (HR) | 61.3 | 68.5 | 64.5 | 70.8 |
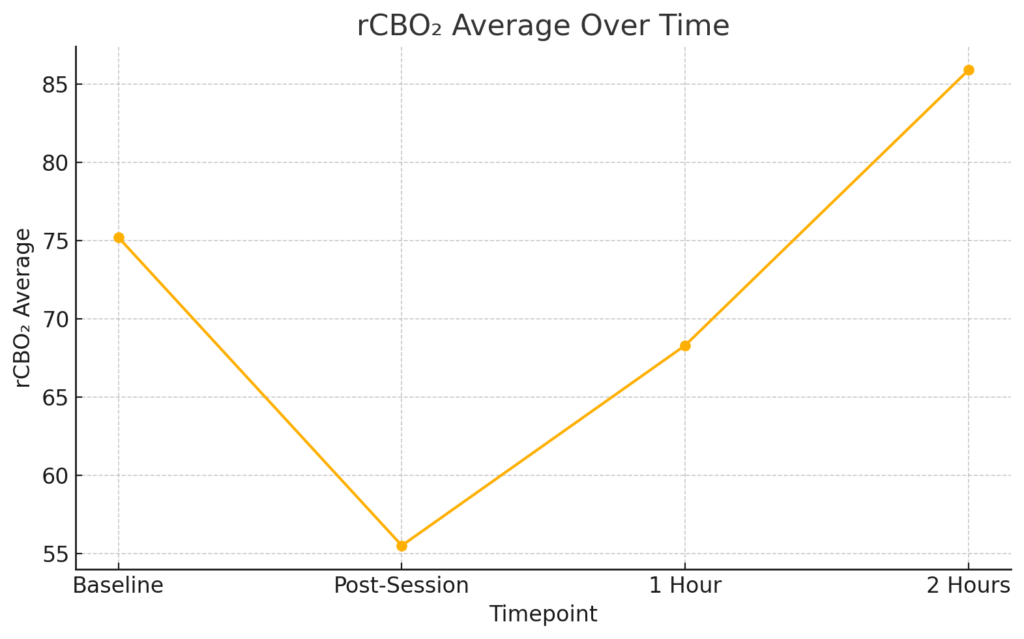
| rCBO₂ Average | 75.2 | 55.5 | 68.3 | 85.9 |
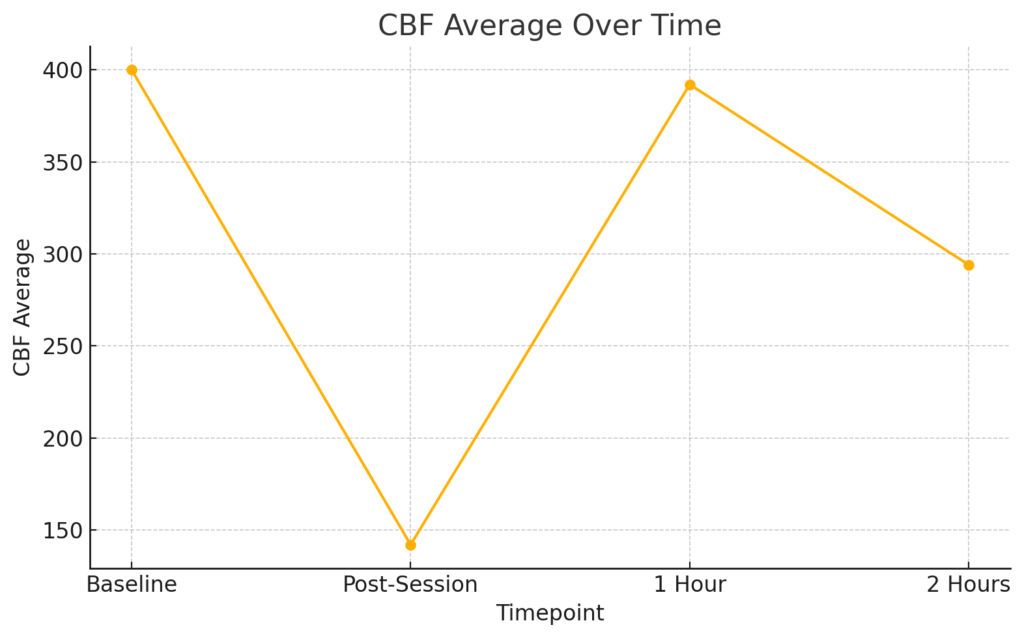
| CBF Average | 400 | 142 | 392 | 294 |
Notes on rCBO₂ Interpretation:
- Normal rCBO₂ values are expected between 50 and 150.
- Values above 70 can suggest increased cortical activity, often associated with mental effort, cognitive load, or stress.
- A decrease in rCBO₂ may indicate relaxation or reduced mental workload.
Analytical Summary:
Baseline:
- Heart rate was within normal range.
- rCBO₂ average was above 70, potentially suggesting a state of mental engagement or mild cognitive stress.
- CBF average was high.
Immediate Post-Session:
- HR increased modestly.
- rCBO₂ dropped substantially, indicating a possible immediate relaxation response.
- CBF average also decreased sharply.
1 Hour Post-Session:
- HR slightly reduced compared to post-session.
- rCBO₂ partially recovered but remained lower than baseline, suggesting sustained relaxation effects.
- CBF average returned close to baseline levels.
2 Hours Post-Session:
- HR increased slightly again.
- rCBO₂ average exceeded baseline, indicating a return to higher cortical activity.
- CBF remained moderately high.
Subjective Feedback:
The participant reported feeling gradually more relaxed after the vibroacoustic session.
The relaxation effect after the session with a progressive return to normal stress levels over time.
Interpretation:
The vibroacoustic session appeared to induce an immediate relaxation response, as evidenced by the drop in rCBO₂ and CBF.
Over time, the participant showed a progressive return to baseline physiological and subjective stress levels.
These results are consistent with the known relaxation-inducing effects of vibroacoustic therapy.