Understanding Brainwave Entrainment and Its Impact on Mental States
Brainwave entrainment is a fascinating field of study that explores how specific methods can synchronize brainwave patterns, leading to various mental states and potential therapeutic benefits. Here’s a look at the proposed methods to achieve brainwave entrainment and how different brainwave frequencies are associated with distinct mental states.
Methods of Brainwave Entrainment
- Sensory Stimulation
Sensory stimulation involves presenting an external rhythmic stimulus to the brain to synchronize its oscillatory activity. This method can be effective during both wakefulness and sleep. For instance, rhythmic auditory stimulation can target sleep-specific oscillatory patterns, which are being investigated for their role in memory consolidation. (Hanslmayr et al., 2019).
Auditory and Visual Stimuli
Binaural Beats (BB)
Binaural beats are created by presenting two slightly different frequencies to each ear, causing the brain to perceive a third tone. This phenomenon results from combined neural activity in the auditory pathway and involves the superior olivary complex (Ingendoh et al., 2023).
Monaural Beats (MB)
Monaural beats are presented to one ear and create beat perception through actual sound wave interference at the cochlear level. Both binaural and monaural beats are popular methods for auditory brainwave entrainment (Ingendoh et al., 2023).
Isochronic Tones
Isochronic tones are characterized by evenly spaced intervals of sound, creating a rhythmic beat with a frequency determined by the length of these intervals. Like monaural tones, isochronic tones are combined into a cohesive auditory experience before reaching the ear (Engelbregt et al., 2019).
Light Flickering
Photic stimulation by external Light flickering uses rhythmic visual stimuli to entrain brainwaves. By flashing lights at specific colors (wavelength), luminance intensity, and flickering frequencies, this method can induce brainwave synchronization (Park et al., 2022). This technique can be used in conjunction with auditory stimuli to enhance the entrainment effect.
- Transcranial Electric Stimulation (tES)
Transcranial electric stimulation (tES) applies weak electrical currents via scalp electrodes to modulate brain activity through resonance. This method includes:
Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation (tDCS): Uses static currents and is non-rhythmic.
Transcranial Alternating Current Stimulation (tACS): Uses oscillating waveforms to influence neural activity.
Each technique varies in its ability to affect brain oscillations, with combined approaches offering a range of effects (Hanslmayr et al., 2019).
- Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (rTMS)
rTMS uses magnetic pulses to induce neural currents with high spatial specificity, making it ideal for targeting specific brain regions and rhythms. It can induce action potentials and, when used with two rTMS coils, allows for network-level testing of brain oscillations (Hanslmayr et al., 2019).
- Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS)
DBS is a more invasive method, typically used in clinical settings for neurological or psychiatric conditions like epilepsy. It involves directly applying electrical currents to brain tissue and allows for both recording from and stimulating various brain regions. Despite its clinical use, the precise physiological and behavioral effects of DBS are still not fully understood (Hanslmayr et al., 2019).
Mental States and Brainwave Frequencies
Different brainwave frequencies are associated with specific mental states and can be selected for brainwave entrainment based on the desired treatment goal.
-
- Delta Waves (0.5-4 Hz): Deep sleep and restorative processes.
- Theta Waves (4-8 Hz): Light sleep, relaxation, and meditation.
- Alpha Waves (8-12 Hz): Relaxed wakefulness and creative thinking.
- Beta Waves (12-30 Hz): Active thinking, focus, and problem-solving.
- Gamma Waves (30-100 Hz): High-level information processing and cognitive functioning.
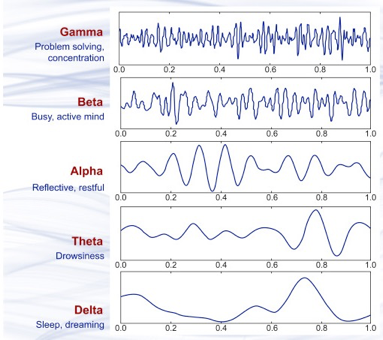
Source: Abhang et al., 2016.
By understanding and harnessing these frequencies through various brainwave entrainment methods, researchers and clinicians aim to promote mental health, improve quality of life, and cognitive enhancement. Brainwave entrainment offers a promising avenue for exploring how synchronized brain activity can influence mental states and potentially provide therapeutic benefits. Whether through non-invasive methods like sensory stimulation and tES or more direct invasive approaches like DBS, the potential for improving mental well-being is significant.
References
Abhang PA, Gawali BW, Mehrotra SC. Technological Basics of EEG Recording and Operation of Apparatus. Introduction to EEG- and Speech-Based Emotion Recognition. 2016: 19–50. doi:10.1016/b978-0-12-804490-2.00002-6
Engelbregt H, Meijburg N, Schulten M, Pogarell O, Deijen JB. The Effects of Binaural and Monoaural Beat Stimulation on Cognitive Functioning in Subjects with Different Levels of Emotionality. Adv Cogn Psychol. 2019 Aug 30;15(3):199-207. doi: 10.5709/acp-0268-8.
Hanslmayr S, Axmacher N, Inman CS. Modulating Human Memory via Entrainment of Brain Oscillations. Trends in Neurosciences. 2019; 42(7): 485–499. doi:10.1016/j.tins.2019.04.004
Ingendoh RM, Posny ES, Heine A. Binaural beats to entrain the brain? A systematic review of the effects of binaural beat stimulation on brain oscillatory activity, and the implications for psychological research and intervention. PloS one, 2023;18(5): e0286023. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0286023
Park Y, Lee K, Park J, Bae JB, Kim SS, Kim DW, Woo SJ, Yoo S, Kim KW. Optimal flickering light stimulation for entraining gamma rhythms in older adults. Sci Rep. 2022 Sep 16;12(1):15550. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-19464-2.
