Assessment of the impact of novel therapy on key cardiometabolic variables
Abstract
This study examined metabolic changes measured by the PNOĒ metabolic analyzer in healthy individuals before and after a 20-minute NanoVi® session. NanoVi® is a bio- optimization device designed to enhance cellular and mitochondrial function, while PNOĒ is a validated cardio-metabolic analyzer capable of measuring 23 biomarkers used in clinical metabolic assessments.
Methods: 10 subjects of various fitness levels participated in the experiment that included a resting and active cardio-metabolic assessment with the PNOĒ device before and after exposure to a 20-minute session with the NanoVi® device. Pre and post resting metabolic tests lasted for 8 – 10 minutes whereas pre and post metabolic tests lasted 10 – 12 minutes. Active metabolic tests which lasted 15 minutes were conducted on a cycle ergometer and included a gradual increase in power output from 60 watts to a power output that yielded 8 out of 10 on the rate of perceived exertion scale for participants. After the post-exercise test, subjects rested for 5 minutes before beginning the NanoVi® treatment. The re-test was conducted within a few minutes of completing the NanoVi® session. During the NanoVi® sessions, subjects sat on a comfortable chair in a fully relaxed position and breathed normally while being connected to the nasal cannula of the NanoVi® device.
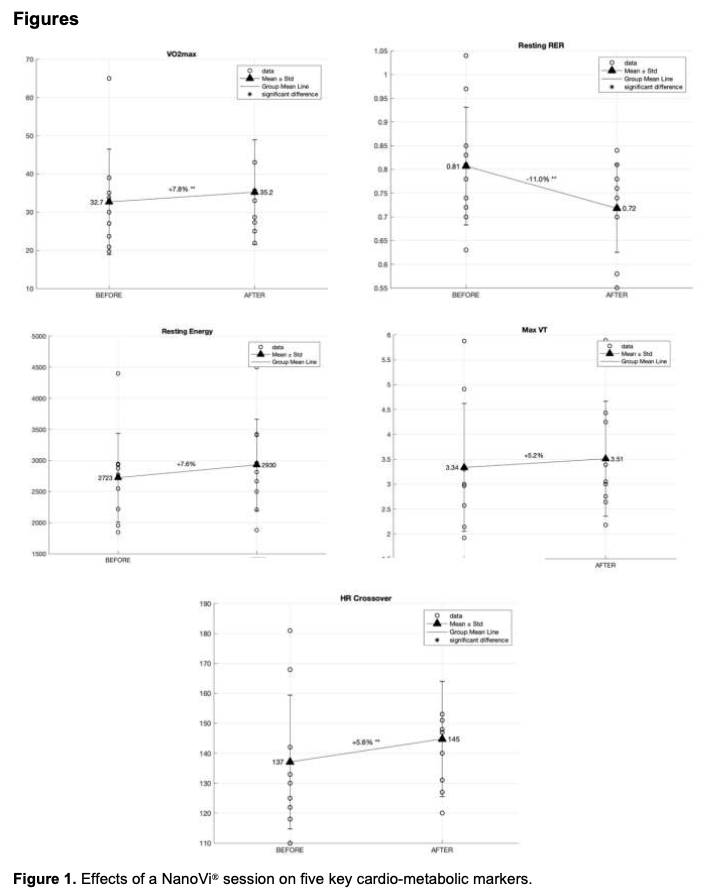
Results: Statistically significant improvements were observed in VO2 max, resting RER, and crossover point, indicating enhanced fat-burning efficiency and metabolic flexibility. Positive trends were also observed in resting metabolic rate (RMR) and tidal volume (VT), though not statistically significant.
Fitter individuals (higher baseline VO2 max) showed more pronounced benefits, likely due to greater capillary density and oxygen absorption capacity.
Three of the five key cardio-metabolic variables showed significant improvements, supporting the potential metabolic benefits of NanoVi® therapy.
Conclusion: A 20-minute NanoVi® session led to significant metabolic improvements, particularly in fat oxidation, aerobic capacity, and metabolic efficiency. The data suggest that fitter individuals respond more strongly to NanoVi® therapy, potentially due to better oxygen utilization and capillary density. These findings highlight NanoVi®’s potential to enhance metabolic function, warranting further research.